
网站救助计划
1.为阅读体验,本站无任何广告,也无任何盈利方法,站长一直在用爱发电,现濒临倒闭,希望有能力的同学能帮忙分担服务器成本
2.捐助10元及以上同学,可添加站长微信lurenzhang888,备注捐助,网站倒闭后可联系站长领取本站pdf内容
3.若网站能存活下来,后续将会持续更新内容
题目描述
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
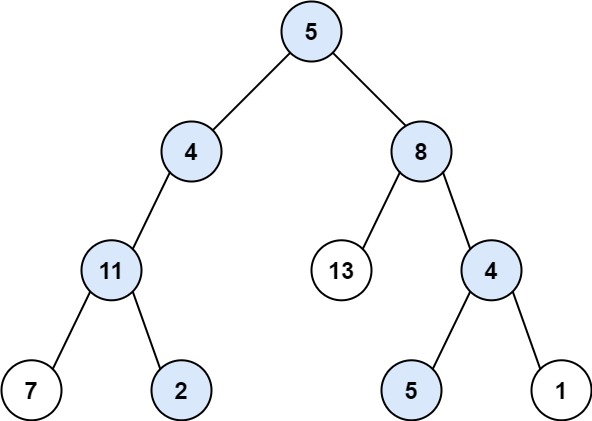
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
输出:[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]示例 2:
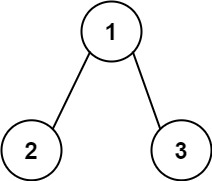
输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
输出:[]示例 3:
输入:root = [1,2], targetSum = 0
输出:[]提示:
- 树中节点总数在范围 [0, 5000] 内
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
- -1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
题解
(递归,前序遍历) O(n)
使用前序遍历的顺序遍历二叉树,遍历一个节点将其加入到路径数组 path 中,如果当前节点是叶子节点且路径和 sum + root->val = target,则说明在树中找到了一条满足路径,将当前路径加入到答案中,继续递归处理左子树和右子树,最后不要忘了 path 数组回溯。
时间复杂度
O(n)
空间复杂度
最坏情况下,叶子节点的个数为 O(2^{n – 1}),其中 n 是二叉树的层数,每个叶子节点对应一个方案,每个方案上的节点个数是 n,所以总时间复杂度为 O(n*2^{n – 1})
C++ 代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int> path;
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int sum, int target) {
if (!root) return;
path.push_back(root->val);
if (!root->left && !root->right && sum + root->val == target) {
ans.push_back(path);
}
dfs(root->left, sum + root->val, target);
dfs(root->right, sum + root->val, target);
path.pop_back();
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int target) {
if (!root) return ans;
dfs(root, 0, target);
return ans;
}
};Java 代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) {
return ans;
}
dfs(root, 0, targetSum);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int sum, int target) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
path.add(root.val);
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && sum + root.val == target) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
dfs(root.left, sum + root.val, target);
dfs(root.right, sum + root.val, target);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}Python 代码
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
self.ans = []
self.path = []
def dfs(node, curr_sum, target):
if not node:
return
self.path.append(node.val)
if not node.left and not node.right and curr_sum + node.val == target:
self.ans.append(self.path[:])
dfs(node.left, curr_sum + node.val, target)
dfs(node.right, curr_sum + node.val, target)
self.path.pop()
if not root:
return self.ans
dfs(root, 0, targetSum)
return self.ans本文由读者提供,Github地址:https://github.com/tonngw
点击面试手册,获取本站面试手册PDF完整版